| ☰ See All Chapters |
Spring @Bean’s initMethod and destroyMethod Attributes Example
In this tutorial you will learn spring example to use initMethod and destroyMethod attributes of the @Bean annotation to perform certain actions after bean initialization and before bean destruction by container respectively. initMethod and destroyMethod attributes of the @Bean annotation can be replaced by javax.annotation.PostConstruct, javax.annotation.PreDestroy annotations. These two annotations are removed from java 9. In java 8 and below versions @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations could be used for spring bean life cycle management.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.java4coding</groupId> <artifactId>Spring3_initMethodAndDestroyMethodAttributesInBean</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>Spring3_initMethodAndDestroyMethodAttributesInBean</name> <url>https://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <org.springframework.version>3.0.0.RELEASE</org.springframework.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> |
FileService.java
package com.java4coding;
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException;
public class FileService {
BufferedReader reader = null; String text = "";
public void init() { try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt")); text = reader.readLine(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("-----------init() method : File Initialized. ------------"); }
public void destroy() { try { if (reader != null) { reader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("-----------destroy() method : File Closed. ------------"); } } |
SpringConfiguration.java
package com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.java4coding.FileService;
@Configuration public class SpringConfiguration {
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy") public FileService fileService() { return new FileService(); } } |
Demo.java
package com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
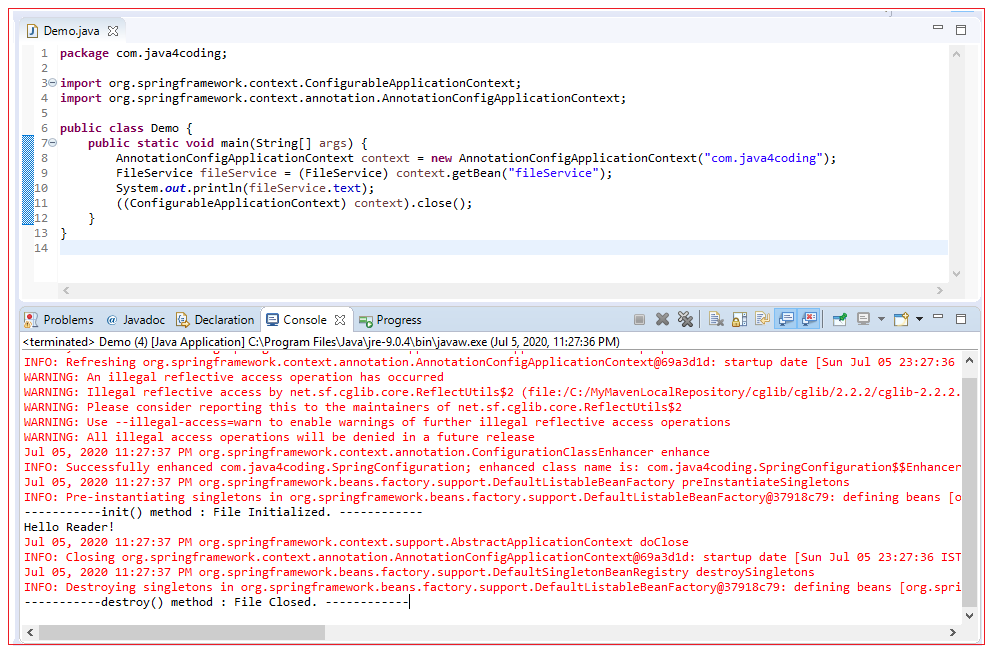
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.java4coding"); FileService fileService = (FileService) context.getBean("fileService"); System.out.println(fileService.text); ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).close(); } } |
Project Directory Structure
Output:
All Chapters

